VPD Chart: A Guide to Understanding and Optimizing Plant Growth
Understanding the VPD Chart: A Key to Optimizing Plant Growth
When it comes to indoor gardening, precision is key. One of the most important metrics that advanced growers use to ensure optimal plant growth is the Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD). Understanding how to read and utilize a VPD chart can make all the difference in your plants’ health, productivity, and overall success. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what a VPD chart is, how it works, and how you can use it to your advantage for indoor plant cultivation.

What is Vapor Pressure Deficit (VPD)?
Before we dive into the VPD chart itself, it’s essential to understand what VPD actually is. Vapor Pressure Deficit represents the difference between the amount of moisture in the air and the amount of moisture that the air can hold when it’s fully saturated. In simpler terms, it’s a measure of how much the air "wants" to take water from the plant. VPD is a crucial metric because it helps determine the rate of transpiration (water evaporation) from the plant leaves.
Why is VPD Important for Plants?
VPD plays a significant role in plant growth because it directly impacts the plant’s transpiration rate. If the VPD is too low, plants may not transpire enough, leading to reduced nutrient uptake and sluggish growth. Conversely, if the VPD is too high, plants may lose too much water, leading to stress, wilting, and potential nutrient deficiencies. Striking the right balance is crucial, and this is where the VPD chart comes into play.
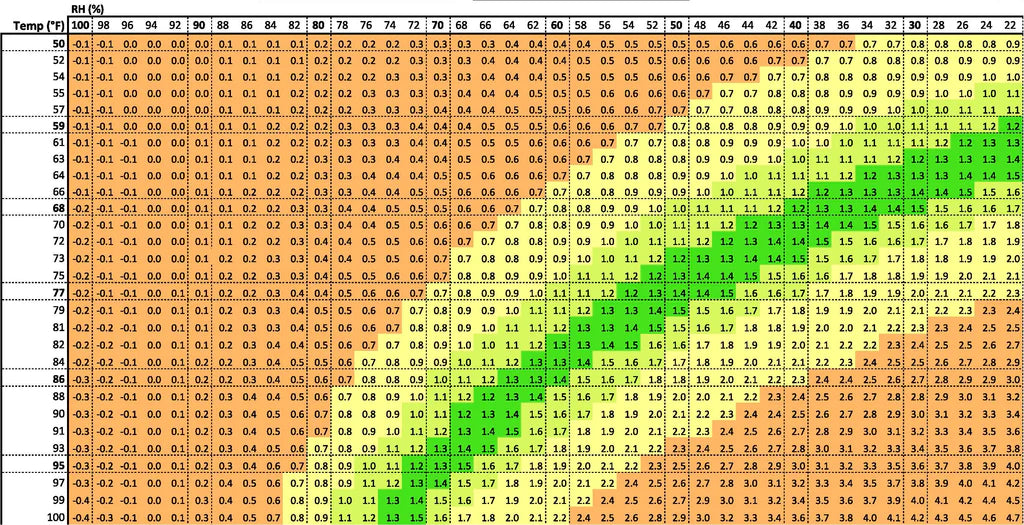
How to Read a VPD Chart
A VPD chart helps growers visualize the ideal vapor pressure deficit for specific temperature and humidity ranges. The chart typically consists of temperature (in either Fahrenheit or Celsius) on the horizontal axis and relative humidity (RH) on the vertical axis. The chart will display various zones, often color-coded, representing the ideal, acceptable, and dangerous VPD levels for plant growth.
- Temperature: The temperature, whether in Fahrenheit or Celsius, refers to the air temperature around your plants. This is important because warmer air can hold more moisture, which affects the VPD.
- Relative Humidity (RH): RH represents the amount of moisture present in the air compared to the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at a specific temperature.
- VPD Zones: The chart will often indicate optimal VPD zones where plant growth is maximized. Green zones typically represent ideal conditions, while red zones indicate stress.
The Ideal VPD Range for Plant Growth
While the ideal VPD range can vary depending on the plant species and growth stage, most plants thrive in a VPD range between 0.8 and 1.2 kPa (kilopascals). Here’s a breakdown of the optimal VPD range based on growth stages:
- Seedling Stage: Seedlings and young plants prefer a lower VPD, typically between 0.4 and 0.8 kPa. This allows them to retain more moisture, which is crucial for early root development.
- Vegetative Stage: During the vegetative stage, plants can handle a moderate VPD range between 0.8 and 1.2 kPa. This promotes healthy transpiration and nutrient uptake.
- Flowering Stage: In the flowering stage, plants tend to prefer a slightly higher VPD, usually between 1.0 and 1.5 kPa. This encourages the plant to focus energy on producing fruits and flowers.
Common Mistakes When Using a VPD Chart
Even though the VPD chart is a valuable tool, growers sometimes make mistakes when interpreting or applying the data. Here are some common pitfalls:
- Ignoring Plant-Specific Needs: Different plants have different VPD requirements. Always adjust your VPD targets based on the specific needs of your plant species.
- Overlooking Airflow: Proper airflow in your grow environment helps to stabilize temperature and humidity. Without proper circulation, VPD levels can fluctuate unpredictably.
- Not Adjusting for Growth Stages: As mentioned earlier, different growth stages require different VPD levels. Adjust the temperature and humidity as your plants transition from seedlings to full bloom.
How to Control VPD in Your Grow Room
Controlling VPD involves manipulating both temperature and humidity in your grow room. Here’s how you can achieve the optimal VPD range:
- Temperature Control: Use HVAC systems, heaters, or air conditioners to maintain the desired temperature in your grow room. A stable temperature is key to keeping your VPD in check.
- Humidity Control: Dehumidifiers and humidifiers are essential tools for controlling relative humidity. These devices allow you to adjust the air moisture levels as needed to align with your target VPD.
- Airflow and Ventilation: Proper airflow helps prevent hot spots and ensures even temperature and humidity throughout your grow space. Use oscillating fans or inline fans to maintain consistent airflow.
Advanced Techniques for Managing VPD
If you’re looking to fine-tune your grow room even further, there are advanced techniques and tools available to manage VPD more effectively:
- Environmental Controllers: Automated controllers allow you to set specific parameters for temperature and humidity, adjusting them in real-time to maintain the ideal VPD range.
- Monitoring Sensors: Install temperature and humidity sensors at different points in your grow room to get accurate readings. This helps you track and adjust your VPD as necessary.
- Data Logging: Some advanced systems allow you to log environmental data over time. This can provide valuable insights into how your VPD levels are affecting plant growth, allowing you to make more informed decisions.
Conclusion
Understanding and controlling VPD is one of the most effective ways to optimize plant growth in an indoor setting. By learning to read and adjust based on a VPD chart, you can ensure that your plants are receiving the right balance of water and nutrients. Whether you’re growing in a small tent or a large grow room, mastering VPD will take your gardening to the next level.
Remember, VPD isn’t just about numbers—it’s about understanding how your plants interact with their environment. With the right tools, techniques, and knowledge, you can create a grow space that consistently yields healthy, vibrant plants.


